Unit 6.6
Cloud Computing in Business
IT 233: Business Information Systems
Learning Objectives 🎯
By the end of this session, you will be able to:
- ✅ Define cloud computing and explain its core characteristics.
- ✅ Differentiate between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS service models.
- ✅ Describe public, private, and hybrid cloud deployment models.
- ✅ Identify key benefits and challenges of cloud adoption.
- ✅ Provide examples of cloud computing in business.
What is Cloud Computing? ☁️
Definition: Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics—over the internet ("the cloud").
Instead of this...
❌ Buying expensive servers
❌ Maintaining data centers
❌ Hiring IT staff to manage hardware
✅ Pay only for what you use
✅ Scale instantly based on needs
</div>
The Big Three Cloud Providers 🏢
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) - Market leader (~32%)
- Microsoft Azure - Enterprise favorite (~22%)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) - Growing fast (~10%)
Other notable providers:
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
Five Essential Characteristics (NIST)
- On-Demand Self-Service - Provision resources automatically, anytime
- Broad Network Access - Access from any device, anywhere
- Resource Pooling - Multiple customers share resources (multi-tenant)
- Rapid Elasticity - Scale up or down instantly based on demand
- Measured Service - Pay only for what you use (metered billing)
Cloud Service Models
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
The "Pizza as a Service" Analogy 🍕
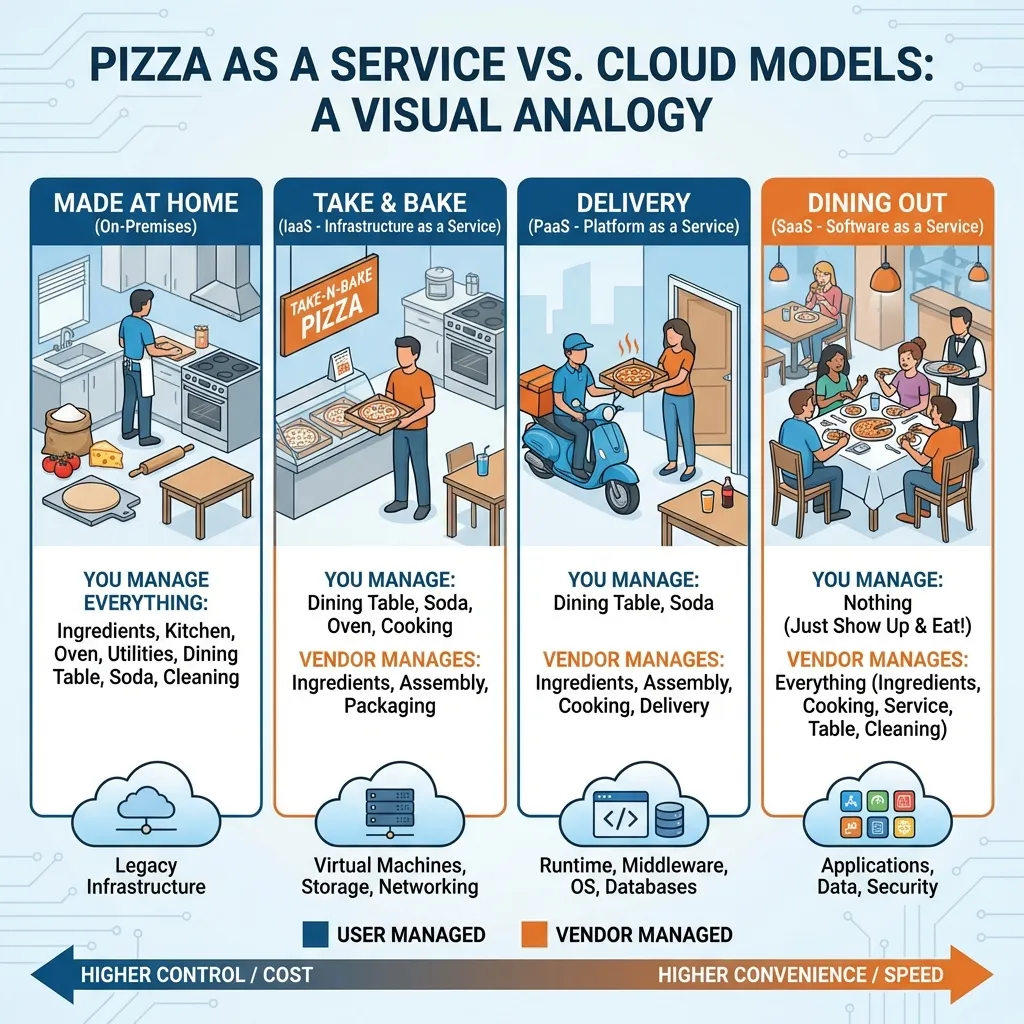
The Pizza Analogy 🍕
On-Premises (Traditional)
Make pizza at home from scratch
You manage: Ingredients, oven, dining table, everything!
Cloud
- IaaS: Take-and-bake pizza (you get raw pizza, bake at home)
- PaaS: Pizza delivery (ready pizza, you serve it)
- SaaS: Dine-in restaurant (everything is done for you)
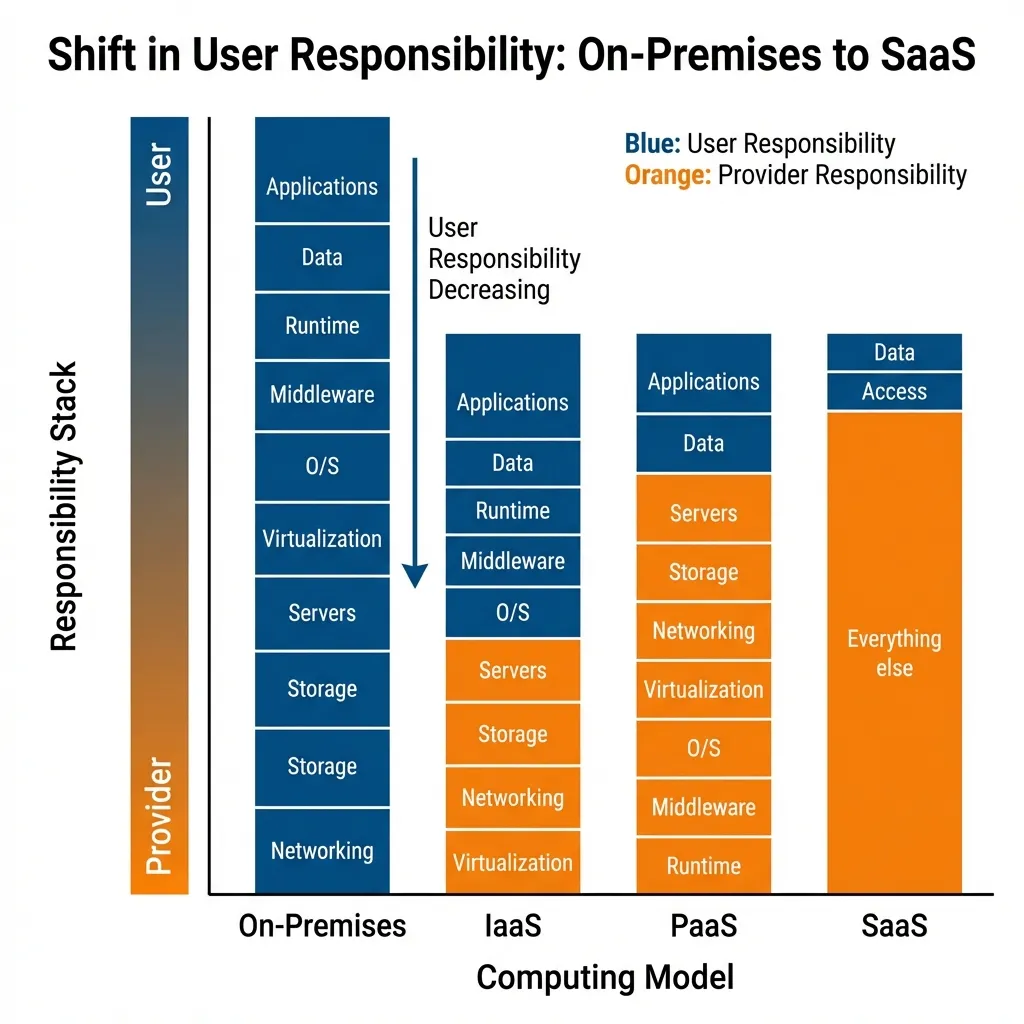
Service Models: The Responsibility Stack
| Layer | On-Premises | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | You | You | You | Provider |
| Data | You | You | You | You |
| Runtime/Middleware | You | You | Provider | Provider |
| Operating System | You | You | Provider | Provider |
| Virtualization | You | Provider | Provider | Provider |
| Servers/Storage/Network | You | Provider | Provider | Provider |
As you move right → Less control, but less management effort!
Service Models: Quick Reference 📊
IaaS - Infrastructure
🏗️ "Rent raw computing power"
👤 For: IT Admins
📌 AWS EC2, Azure VMs
PaaS - Platform
🛠️ "Just deploy your code"
👤 For: Developers
📌 Heroku, Google App Engine
SaaS - Software
💻 "Use it in your browser" | 👤 For: Everyone | 📌 Gmail, Zoom, Salesforce
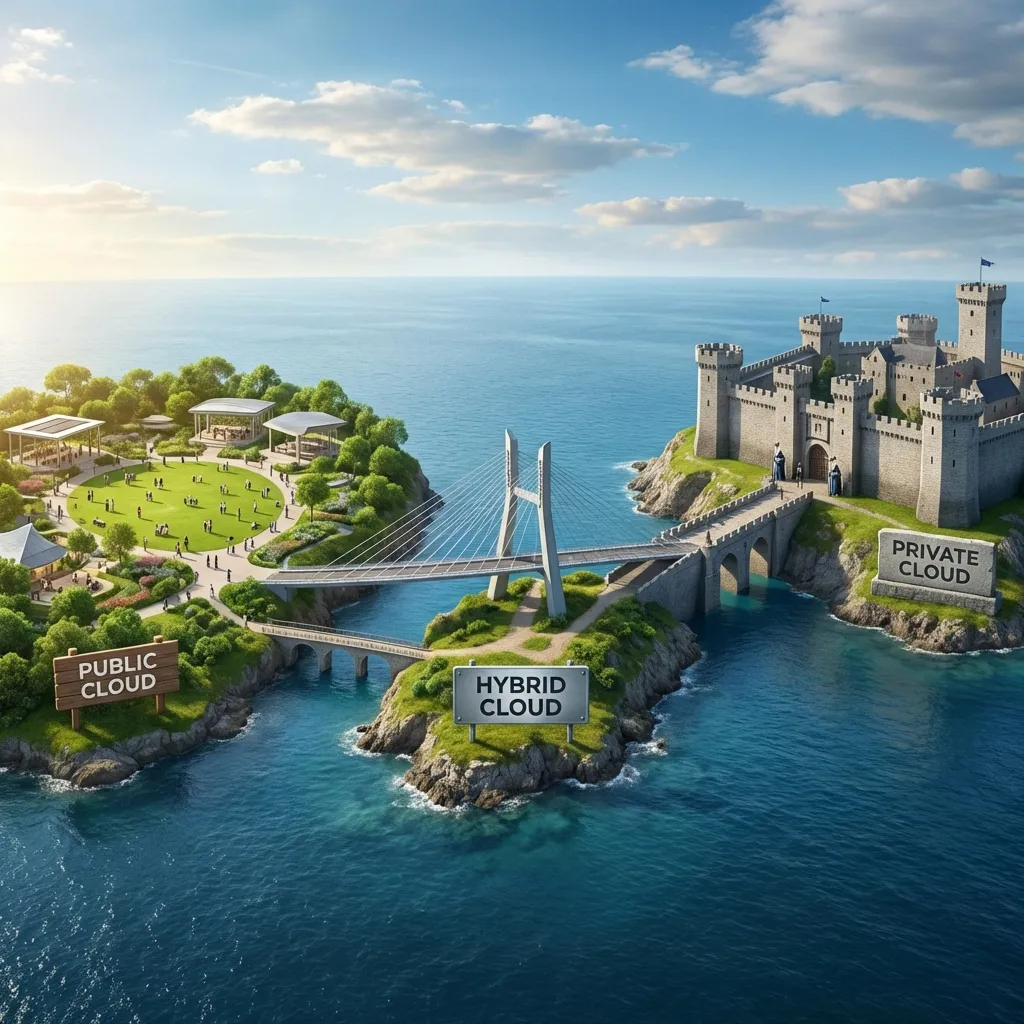
Cloud Deployment Models
Where does your cloud live?
Deployment Models Comparison 📊
| Model | Best For | Key Benefit | Main Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public ☁️ | Startups, web apps | Cost-effective, scalable | Less control, security concerns |
| Private 🔒 | Banks, healthcare, govt | Full control, compliance | Higher cost, needs IT expertise |
| Hybrid 🔀 | Variable workloads | Flexibility, cost optimization | Complex to manage |
💡 Cloud Bursting: Run normal workloads on private cloud, "burst" to public cloud during peak demand

Benefits & Challenges
Why Cloud? Why Not?
Business Benefits of Cloud Computing 💼
- 💰 Cost Reduction - No upfront hardware costs, pay-as-you-go
- 📈 Scalability - Scale up/down instantly based on demand
- ⚡ Speed & Agility - Deploy in minutes, not months
- 🌍 Global Reach - Deploy worldwide with a few clicks
- 🛡️ Disaster Recovery - Built-in backup across multiple locations
- 🔄 Automatic Updates - Always on the latest version
- 🤝 Enhanced Collaboration - Work together from anywhere
Challenges of Cloud Computing ⚠️
- 🔐 Security Concerns - Data on external servers
- ⏸️ Downtime Risk - Internet dependency
- 🔗 Vendor Lock-In - Hard to switch providers
- 📋 Compliance Issues - Meeting regulatory requirements
- 🎛️ Limited Control - Less customization than on-premises
- 💸 Hidden Costs - Data transfer, premium support fees
Real-World Business Applications 🌐
- Netflix: 250M+ subscribers, 15M concurrent streams on AWS
- Zoom: 10M → 300M daily users in 4 months (2020) - cloud elasticity!
- Airbnb: 150M+ users globally, zero data centers built
- Spotify: Analyzes 500M+ user patterns daily on Google Cloud
💡 None of these companies could have scaled this fast with traditional infrastructure
Emerging Cloud Trends 🚀
Serverless Computing
- Run code without managing servers
- Pay per millisecond of execution
- AWS Lambda, Azure Functions
Multi-Cloud Strategy
- Use multiple providers
- Avoid vendor lock-in
- Best service for each workload
Edge Computing
Process data closer to source (IoT, self-driving cars) → lower latency
Cloud Computing in Nepal 🇳🇵
Success Stories ✅
- NIC Asia, Kumari Bank (cloud banking)
- Daraz: 10x traffic during 11.11 sales
- eSewa/Khalti: millions of transactions
- TU: 500K+ students on Microsoft 365
Challenges ⚠️
- 35% internet penetration outside KTM
- No local AWS/Azure data centers
- Data sovereignty concerns
- Cloud skills gap
Quick Quiz! 🧠
Q1: A company wants to run its own servers but have someone else manage the hardware. Which service model?
→ IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Q2: Gmail is an example of which service model?
→ SaaS (Software as a Service)
Q3: A bank wants full control over its data but also wants to use public cloud for its customer-facing website. Which deployment model?
→ Hybrid Cloud
Key Takeaways 📝
- ☁️ Cloud = renting computing power instead of buying (CapEx → OpEx)
- 📊 Service models: IaaS (IT admins), PaaS (developers), SaaS (everyone)
- 🏗️ Deployment: Public (cheap), Private (secure), Hybrid (flexible)
- 🚀 Emerging: Serverless, Multi-cloud, Edge computing
- 🇳🇵 Nepal: Growing adoption, but infrastructure & data sovereignty challenges remain
Discussion Questions 💬
- How would you advise a Nepali SME on choosing between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
- Why might NRB require banks to use private cloud for certain data?
- How can businesses mitigate vendor lock-in using multi-cloud strategies?
- What opportunities does serverless computing create for Nepali developers?
Thank You! 🙏
Questions?
IT 233: Business Information Systems
Unit 6.6: Cloud Computing in Business