Unit 6.4
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems Explained
IT 233: Business Information Systems
Today's Learning Objectives 🎯
By the end of this session, you will be able to:
- ✅ Define ERP and its core concept of integration.
- ✅ Explain how ERP systems solve the problem of information silos.
- ✅ Identify the common modules of an ERP system.
- ✅ Describe the major benefits and challenges of implementation.
The Problem: Information Silos
Before ERP, departments often worked in isolation, creating "information silos."
</div> </div>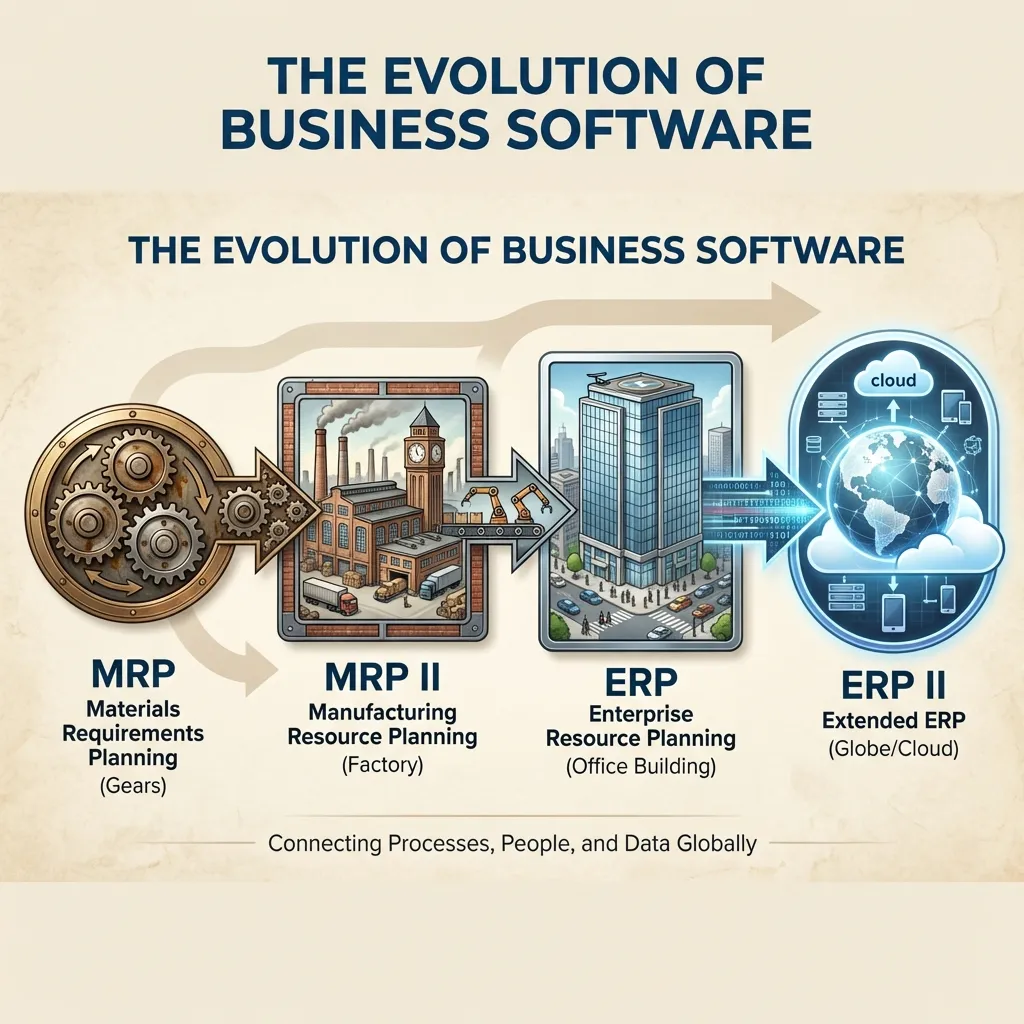
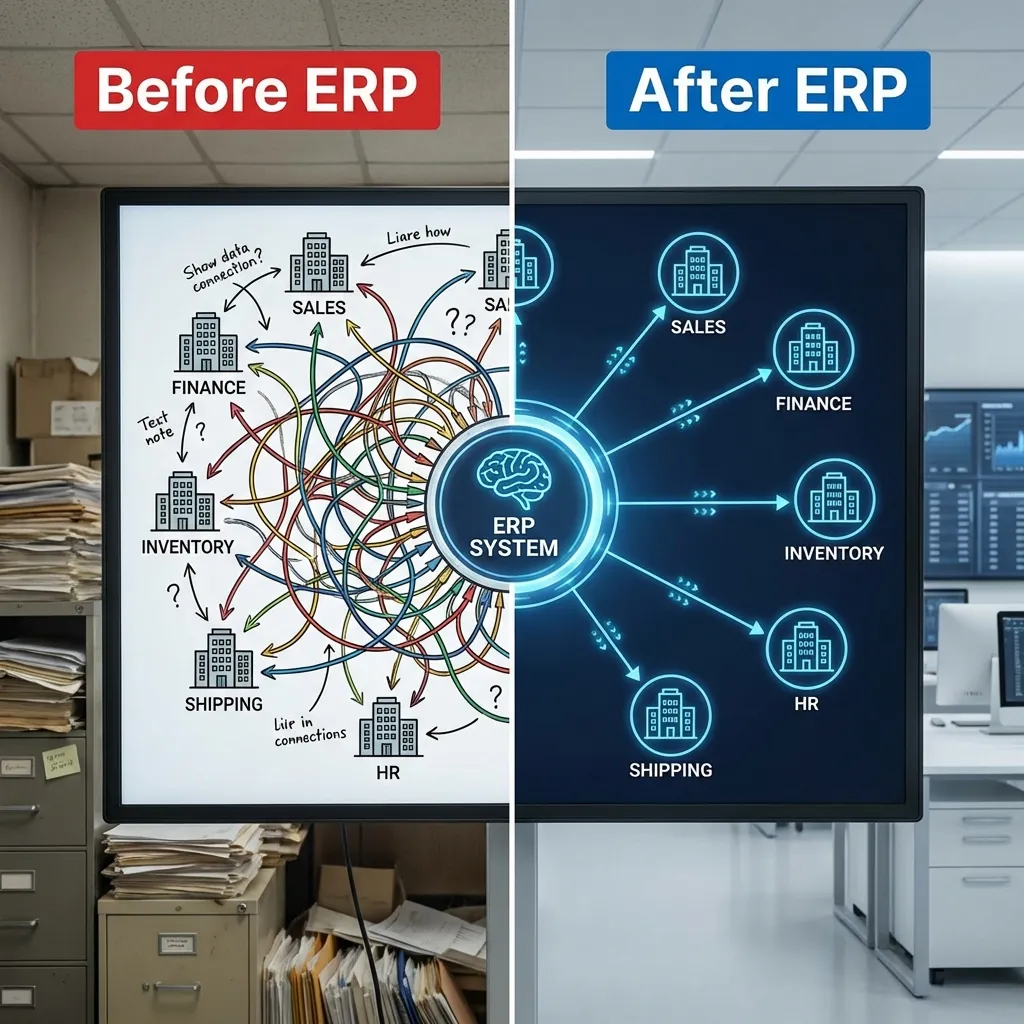
Result: Data duplication, inconsistency, and poor visibility across the business.
The Solution: What is an ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): A suite of integrated software applications that an organization uses to collect, store, manage, and interpret data from many business activities.
- It breaks down information silos by creating a single, unified platform.
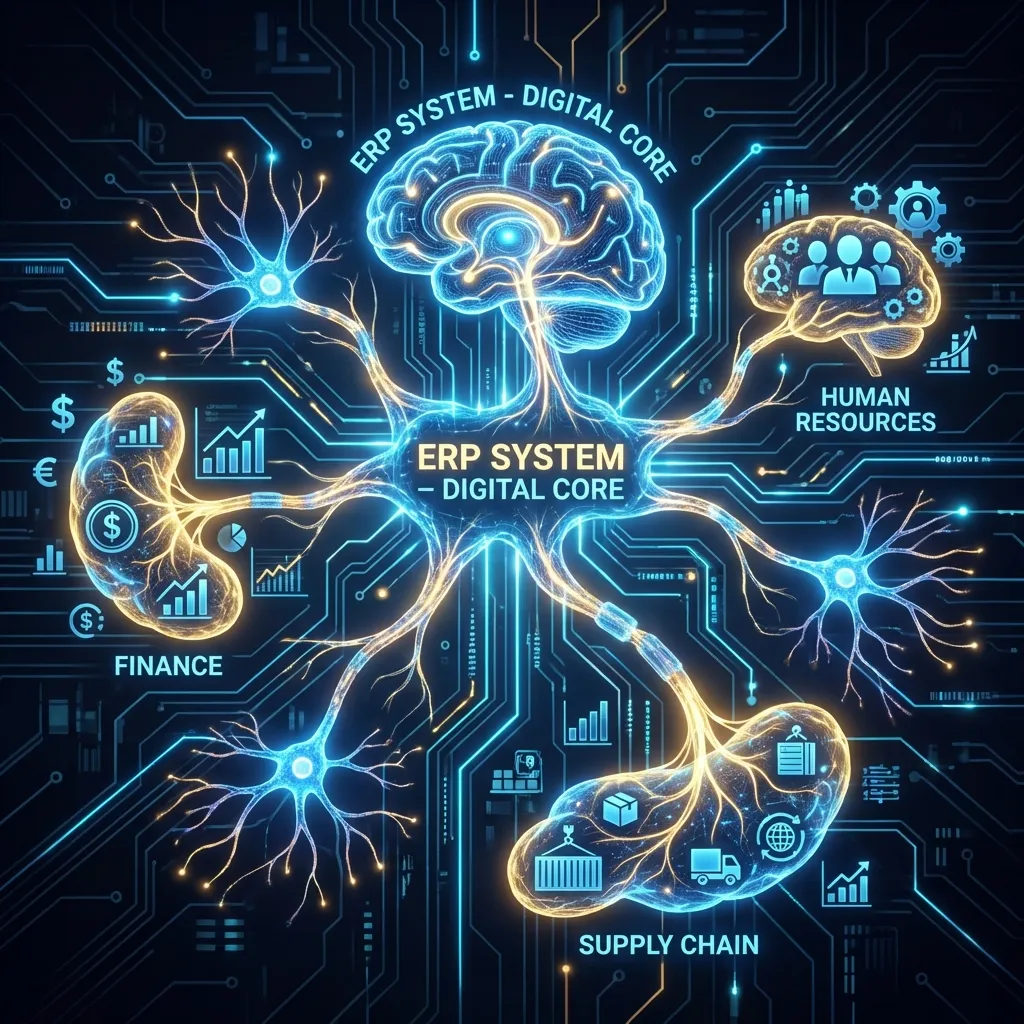
- It acts as the central nervous system for the entire organization.
- Key vendors include SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
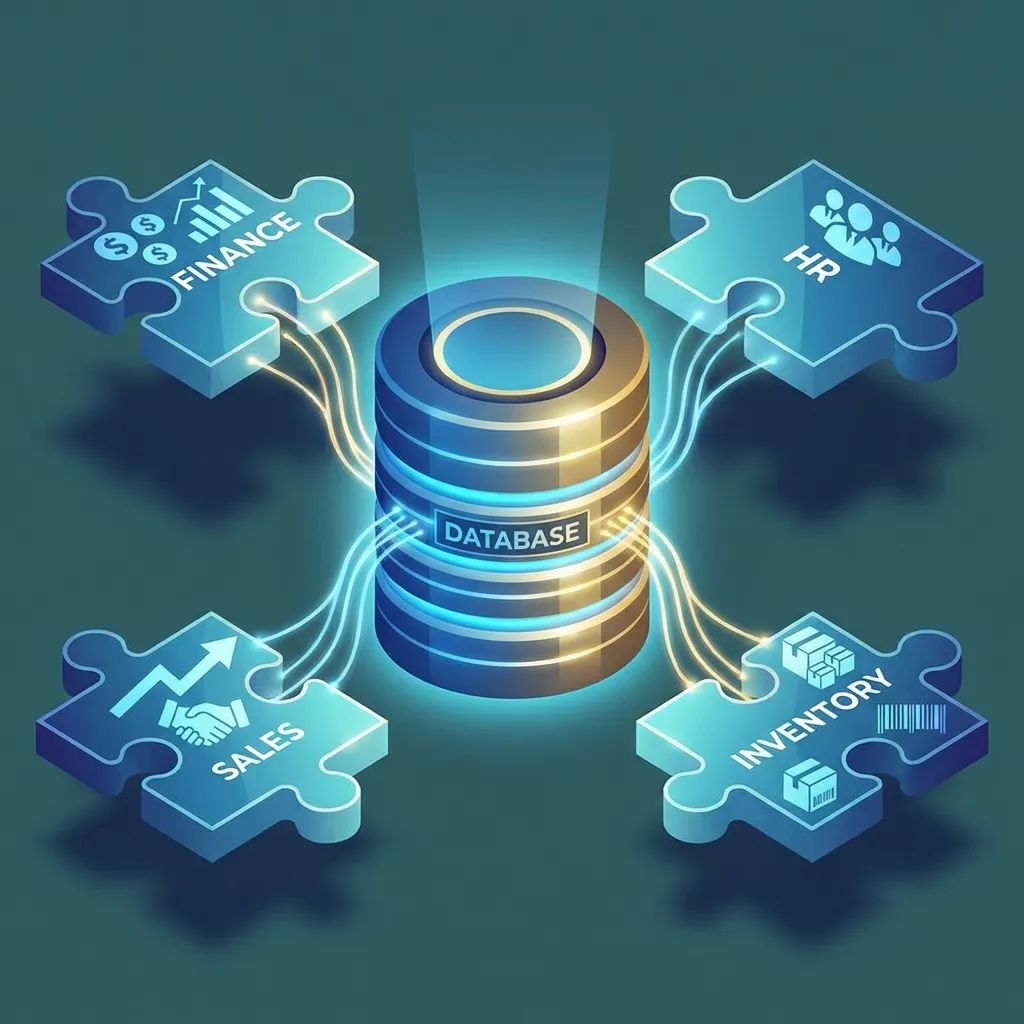

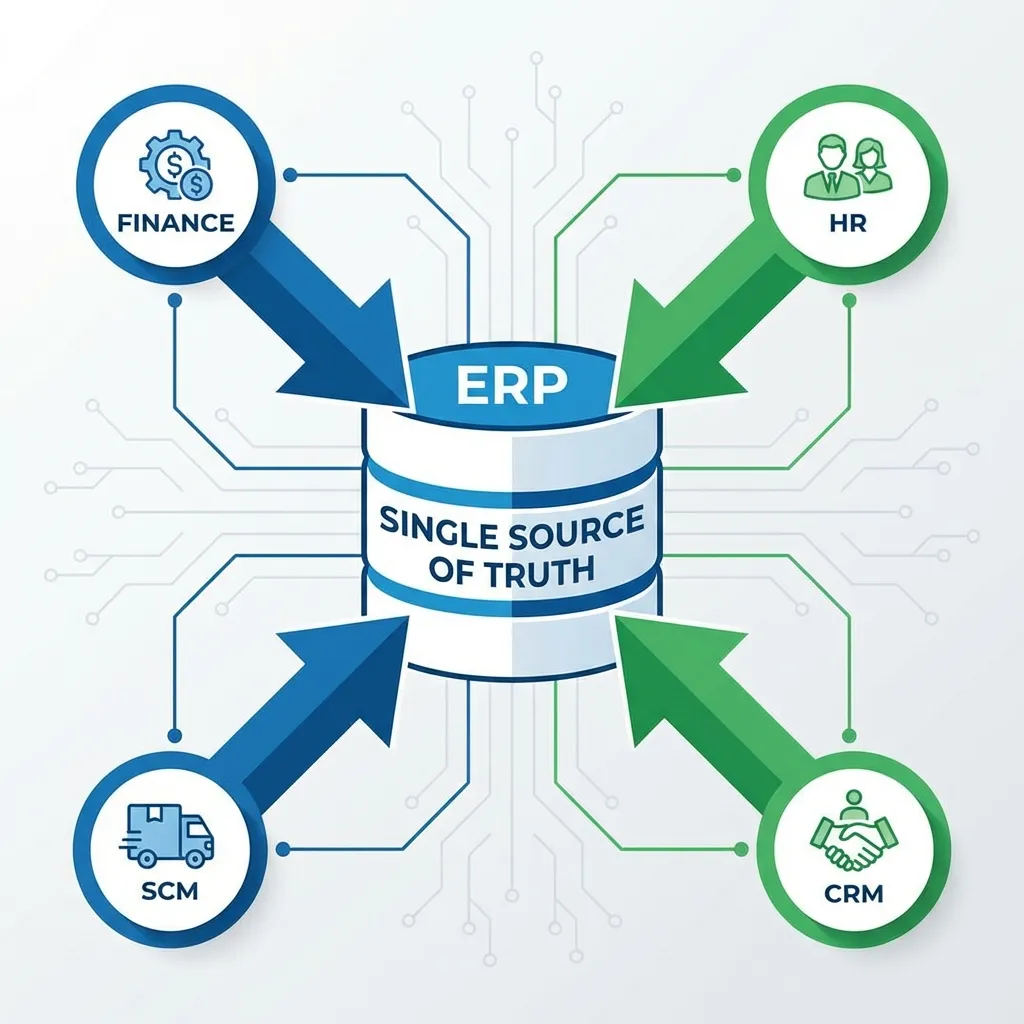
The Core Concept: A Single Source of Truth ⚡
ERPs achieve integration through a central database.
This ensures every department is working with the same, up-to-date information, eliminating guesswork and errors.
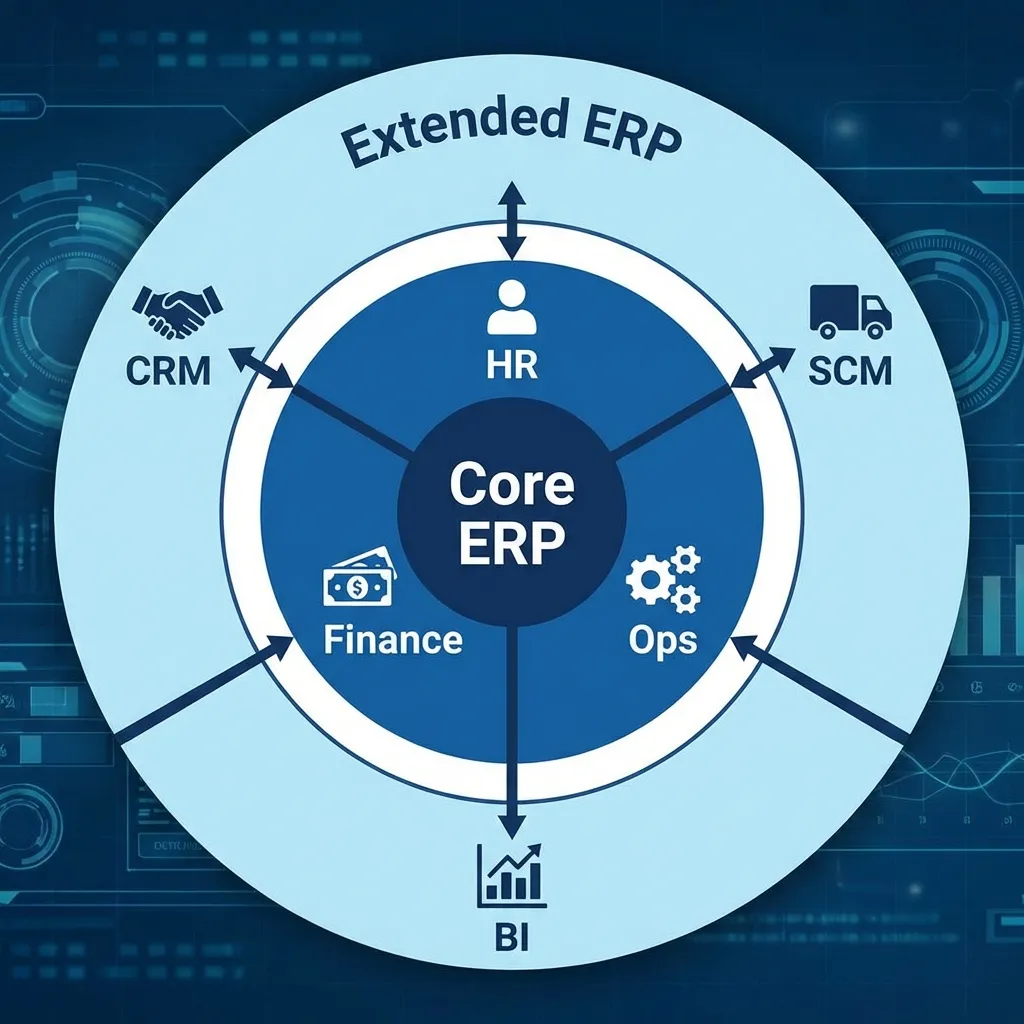
How it Works: An Integrated Workflow
An event in one module automatically triggers updates in others.
Example: Processing a Sales Order
- Sales Module: A new customer order is entered.
- ➡️ SCM Module: Inventory levels are automatically checked and updated. A shipping order is created.
- ➡️ Finance Module: An invoice is generated and the customer's credit is checked.
- ➡️ Management Dashboard: Sales forecasts and revenue reports are updated in real-time.
Key Characteristics of ERP Systems 🔍
- Integrated System: All modules are interconnected and work together seamlessly.
- Central Database: All data is stored in one place, eliminating redundancy and inconsistency.
- Standardized Processes: Adopts industry "best practices," which can improve efficiency but requires organizational change.
- Real-Time Operation: Data is updated instantly across all modules as business transactions occur.
A Look Inside: Common ERP Modules
Financial Management
- General Ledger
- Accounts Payable/Receivable
- Budgeting
Human Capital (HCM)
- Payroll
- Recruiting
- Performance Mgt.
Supply Chain (SCM)
- Inventory Control
- Procurement
- Logistics
Other common modules include Manufacturing and Customer Relationship Management (CRM).

The Two Sides: Benefits vs. Challenges
Benefits 📈
- Improved efficiency & automation
- Better, data-driven decision-making
- Enhanced data security & control
- Increased collaboration between departments
Challenges 📉
- Extremely high cost (software, implementation, maintenance)
- High complexity and long implementation times
- Employee resistance to process changes
- Vendor lock-in makes it hard to switch systems
Practical Application: ERP in Nepal 🇳🇵
Example: A Nepali Hydropower Company
A company like Butwal Power Company could use an ERP to:
- Finance Module: Manage large-scale project budgets, track assets, and handle international investor reporting.
- HCM Module: Manage payroll and training for engineers and staff across multiple remote sites.
- SCM Module: Procure and track high-value equipment (like turbines) from international suppliers.
Result: A unified view of complex operations, improving financial control and project management.
Summary & Key Takeaways 📊
- Integration is Key: ERPs unite all core business functions (finance, HR, SCM) onto a single, shared platform.
- Single Source of Truth: They use a central database to eliminate information silos and ensure data consistency.
- High Risk, High Reward: While benefits like efficiency and better decision-making are immense, implementation is a major undertaking due to high costs, complexity, and the need for organizational change.
Thank You!
Next Topic: Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
We will explore how businesses manage their interactions with current and potential customers.