Database Management Systems (DBMS)
ICT 110: IT for Business
Today's Learning Objectives
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to explain how a DBMS acts as the engine for modern business information systems.
- ✅ Define a DBMS and articulate its core functions for a business.
- ✅ Compare the weaknesses of traditional file systems to the strengths of a DBMS.
- ✅ Differentiate between SQL and NoSQL databases and select the appropriate type for a given business scenario.
- ✅ Identify how DBMS-powered applications (like ERP, CRM) support various business functions.
What is a DBMS?
The Digital Filing Cabinet for Your Business
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software application that allows a business to centrally create, manage, protect, and provide access to its data.
Instead of scattered spreadsheets and documents, a DBMS provides a single, controlled environment.
Its purpose is to transform raw data into a reliable, secure, and accessible corporate asset.
⚡ A DBMS isn't just for storage; it's a system for enforcing business rules and ensuring data quality.

The Problem: Life Before DBMS
Imagine a business running on separate Excel files for each department...
The Mess: Traditional File Systems
📄 Sales Team: customers_sales.xlsx
📄 Accounts Team: customers_billing.xlsx
📄 Shipping Team: customers_shipping.xlsx
The Inevitable Problems
- ❌ Data Redundancy: Same customer address stored in 3 different places.
- ❌ Data Inconsistency: If a customer moves, which file gets updated? All three?
- ❌ No Security: Who can see or change the data? Anyone with the file.
- ❌ No Concurrent Access: What if Sales and Accounts try to update a file at the same time?
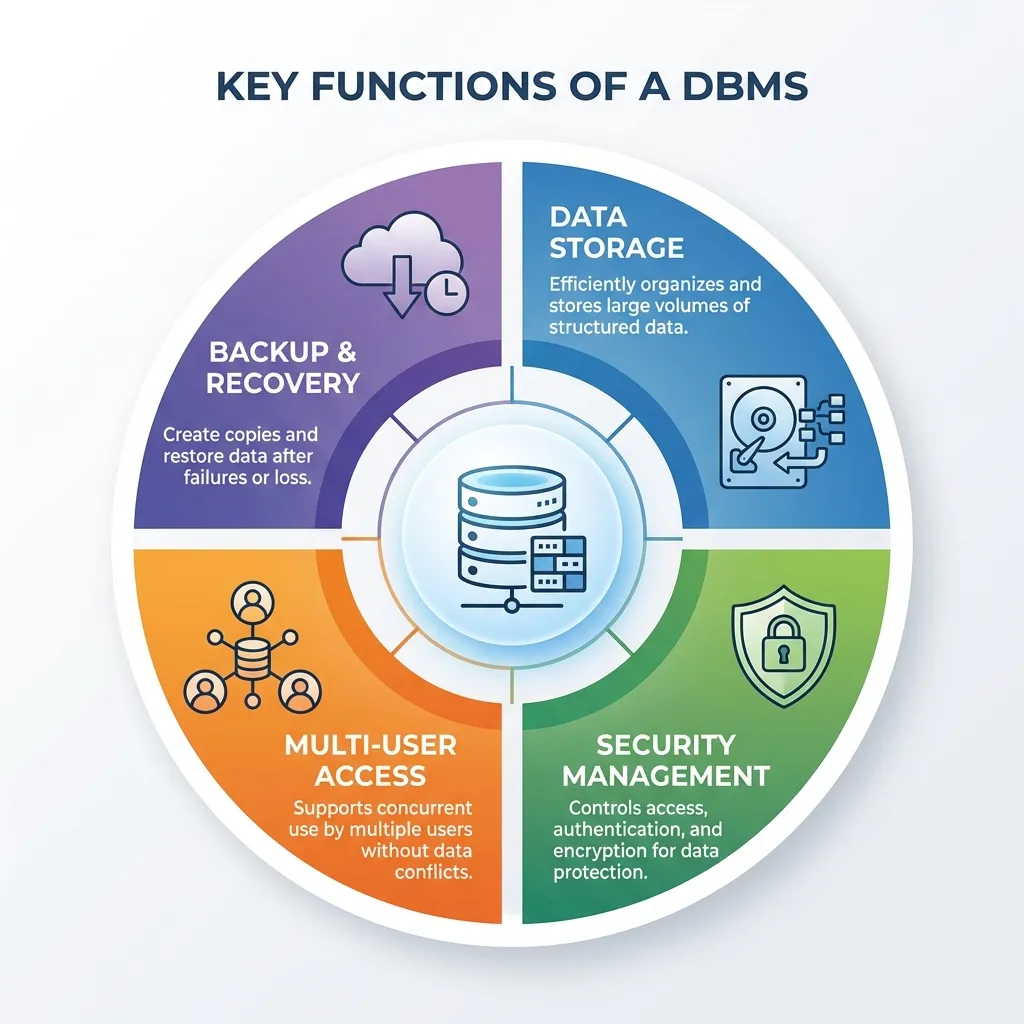
Why Businesses NEED a DBMS
A DBMS solves the problems of traditional file systems by providing critical capabilities:
- 🔍 Data Integrity: Enforces rules to ensure data is accurate and consistent. (e.g., A product quantity cannot be a negative number).
- 🔐 Data Security: Implements robust access controls. An HR manager can view salary data, but a sales associate cannot.
- 🔄 Concurrency Control: Allows multiple users to access and modify data simultaneously without creating conflicts or overwriting each other's work.
- 🗑️ Reduced Redundancy: Establishes a "single source of truth." A customer's address is stored once and shared across departments.
- 💾 Backup and Recovery: Provides mechanisms to protect data from system failures and allows for restoration, ensuring business continuity.
DBMS vs. File System: A Comparison
The difference is between a structured library and a pile of books.
| Feature | Traditional File System | Database Management System (DBMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Redundancy | High (data is duplicated) | Low (controlled and minimized) |
| Data Consistency | Low (updates can be missed) | High (enforced by the system) |
| Security | Limited (OS-level permissions) | Granular (user, role-based access) |
| Multi-User Access | Prone to conflicts | Managed via concurrency control |
| Backup/Recovery | Manual and basic | Automated and sophisticated |
Summary & Key Takeaways
- 🎯 A DBMS is a critical software layer that manages a company's data, ensuring it is secure, consistent, and accessible.
- 🗄️ It overcomes the severe limitations of traditional file systems, such as data redundancy and inconsistency.
- 🔐 Security is not an afterthought; features like access control and auditing are built into the DBMS to protect corporate data assets.
Thank You
Any questions?
Next Topic: Relational Databases and SQL