Unit 4: Computer Networks
Network Security: Firewalls, IPSec, and VPNs
ICT 110: IT for Business
Learning Objectives
- ✅ Firewalls: Protecting the corporate perimeter.
- ✅ IPSec: Locking down data in transit (IPv4 vs IPv6).
- ✅ VPNs: Secure tunneling for remote work.
- ✅ Context: Applying these tools to practical business needs.
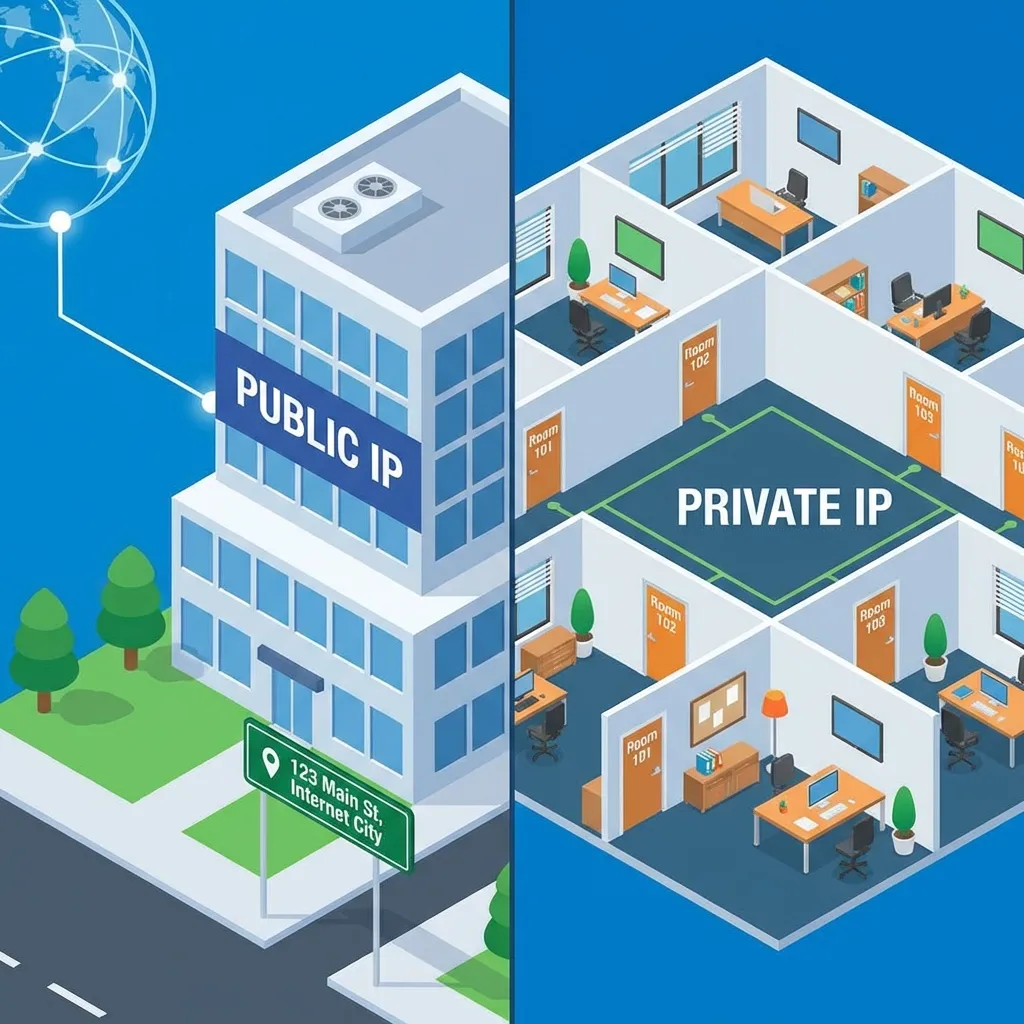
The Context: It Starts with IP Addresses
Security builds directly on the IP Addressing concepts we just learned.
🏢 Public IPs
The "Front Door". Visible to the internet. Needs heavy protection (Firewalls).
🔒 Private IPs
The "Internal Office". Hidden behind the firewall. Requires VPNs to access remotely.
Why Security Matters (The Assets)
What We Protect
- 💰 Finance: Bank details, Payroll.
- 🤝 HR: Personal IDs, Salaries.
- 📊 Marketing: Customer Data.
- ⚙️ Operations: Supply Patterns.
The Risks
- 🔻 Financial Theft
- 🔻 Reputation Loss
- 🔻 Legal Penalties
Visualizing the Defense
1. Firewalls: The Gatekeeper
The Logic:
- "Allow traffic from IP X"
- "Block traffic from IP Y"

Firewalls in Action
Departmental Rules
| 🛡️ Finance | Blocks all external IPs. Only allows internal Accounting Team IPs. |
| 🛡️ HR | Restricts access to confidential employee records. |
| 🛡️ Ops | Only allows trusted Supply Chain Partner IPs. |
The Problem: Data in Transit
Firewalls protect the building (Network). But what happens when data leaves the building?
Scenario: Sending a budget file from Kathmandu HQ to Pokhara Branch over the public internet.
2. IPSec: The Armored Truck
Core Functions
- Authentication: verifies the sender.
- Encryption: Scrambles the content.
IPv4 vs IPv6
- IPv4: IPSec is an add-on (Optional).
- IPv6: IPSec support is built-in (Native).
IPSec Business Use Cases
⚙️ Operations
Securely linking a factory in Birgunj to HQ in Kathmandu.
💰 Banking
Ensuring ATM transaction data cannot be tampered with in transit.
3. VPNs: The Private Tunnel
It gives a remote device (public IP) a temporary presence inside the corporate network (private IP).
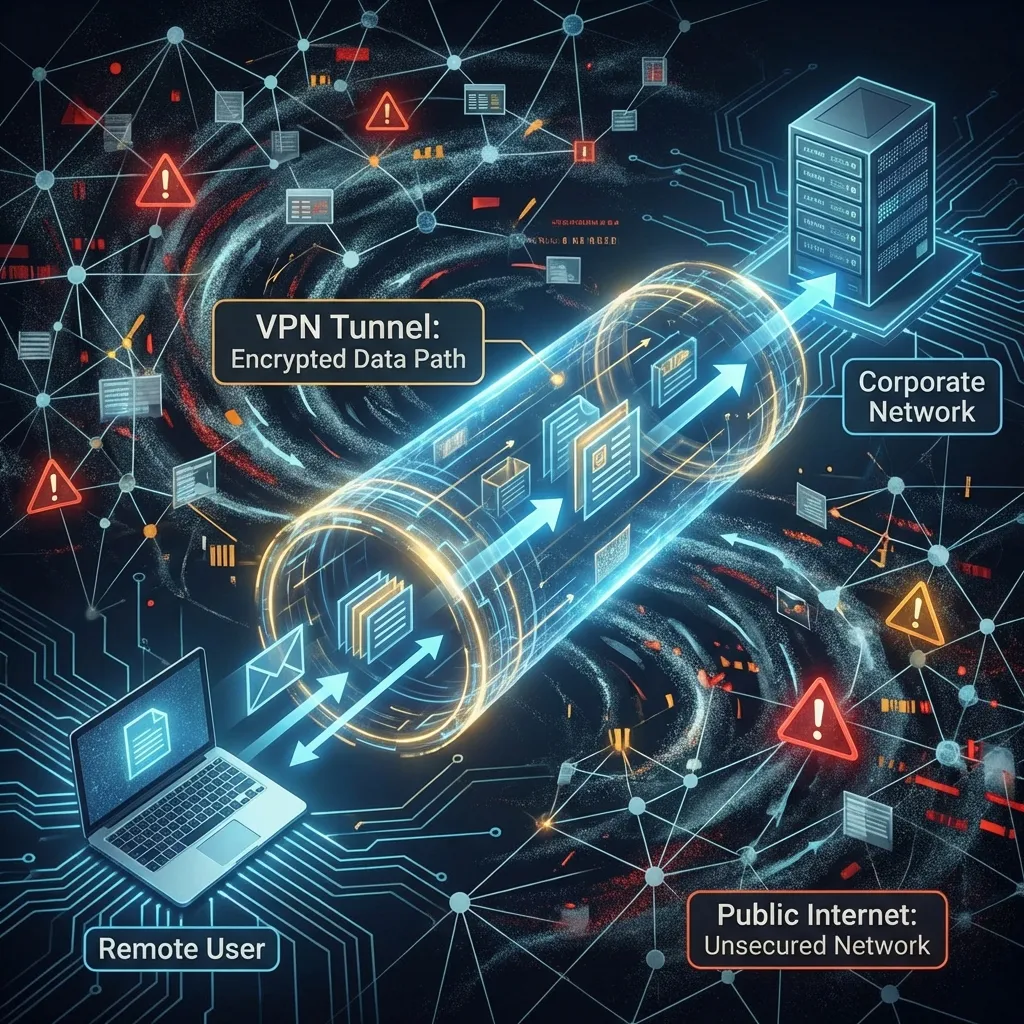
VPNs: Enabling Agility
💼 Remote Work
Working from home with office-level security.
🏢 Branch Links
Cost-effective connection for new retail outlets.
🌍 Access Control
Granting contractors limited access to specific servers.
Nepal Context & Summary 🇳🇵
Local Examples
- eSewa: Heavy firewalling for payments.
- Daraz: VPNs for secure logistics management.
- Banks: IPSec for inter-branch data.
The Security Trio
- Firewall: The Guard (Perimeter)
- IPSec: The Armored Truck (Transit)
- VPN: The Tunnel (Remote Access)
Thank You
Questions?
Next: Databases and Business Data
Next Topic
Continue to:
Introduction to Databases and Business Data →